Understanding the WAL Model
The Work-Applied Learning (WAL) model recognises the workplace as the crucible of learning for change. It has been specifically developed for managers, leaders and entrepreneurs to learn, reflect, introduce change, and be effective in their organisations or communities.
Benjamin Franklin said: “Tell me and I forget, teach me and I may remember, involve me and I learn.” Thus, the WAL model requires the managers, leaders and entrepreneurs to not only learn relevant business and management concepts but actually apply them in a real-life Work-Applied Change projects. This integration of the concepts and their application in the project provides greater understanding and helps managers and entrepreneurs, as change leaders, to embed their learning which can then be applied in other contexts.
WAL extends Work-Based Learning (WBL) by incorporating action research and action learning, in addition to reflective practice, enabling organisational learning, knowledge creation, and change beyond individual and departmental improvements.
Empowering managers, leaders and intrepreneurs to change through Work-Applied Learning process.
Work-Based Learning Features
The foundation upon which Work-Applied Learning is built
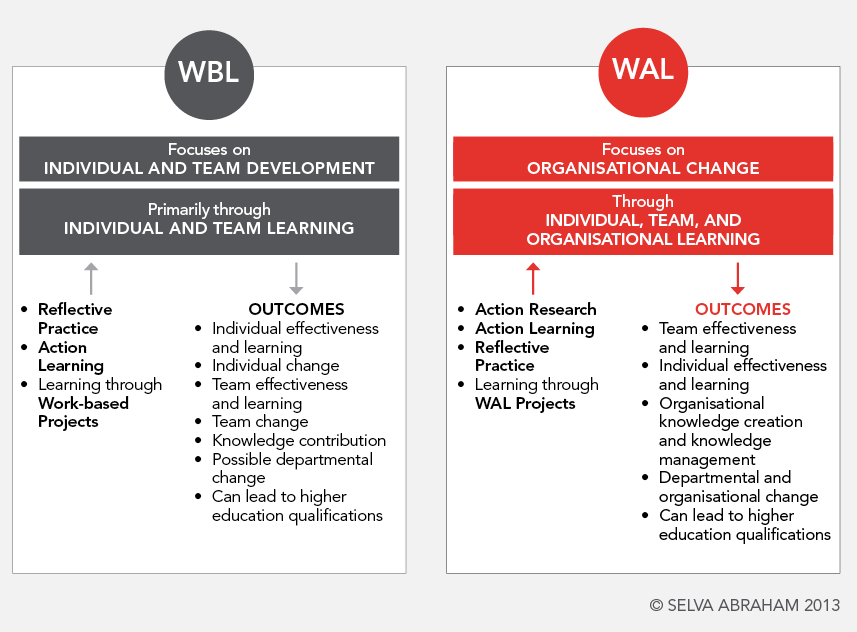
- Focuses on learning through work-oriented projects
- Often collaborative and trans-disciplinary
- Practical yet higher-level cognitive process
- Learned by working, not just reading or observing
- Learner-centered with workplace facilitators
- Involves learning teams and facilitator guidance
- Enables critical analysis and reflective thinking
- Creates knowledge through collective activities
- Integrates business concepts with interpersonal skills
- Can lead to professional practice certifications
Four Phases of WAL
The progressive stages of Work-Applied Learning
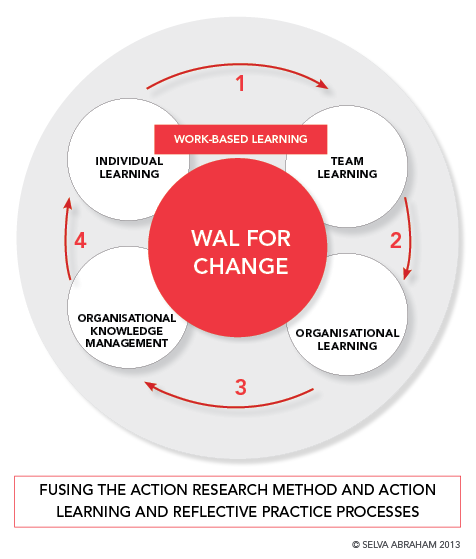
Phase 1
Individual Learning
Personal skill development and critical reflection on work practice and experience.
Phase 2
Team Learning
Collaborative learning within teams through action learning sets and group reflection.
Phase 3
Organisational Learning
Learning that impacts the whole organisation through systemic change initiatives.
Phase 4
Knowledge Creation
Creating and managing new organisational knowledge through practitioner research.
The WAL Formula
A consultative summary of the Work-Applied Learning process
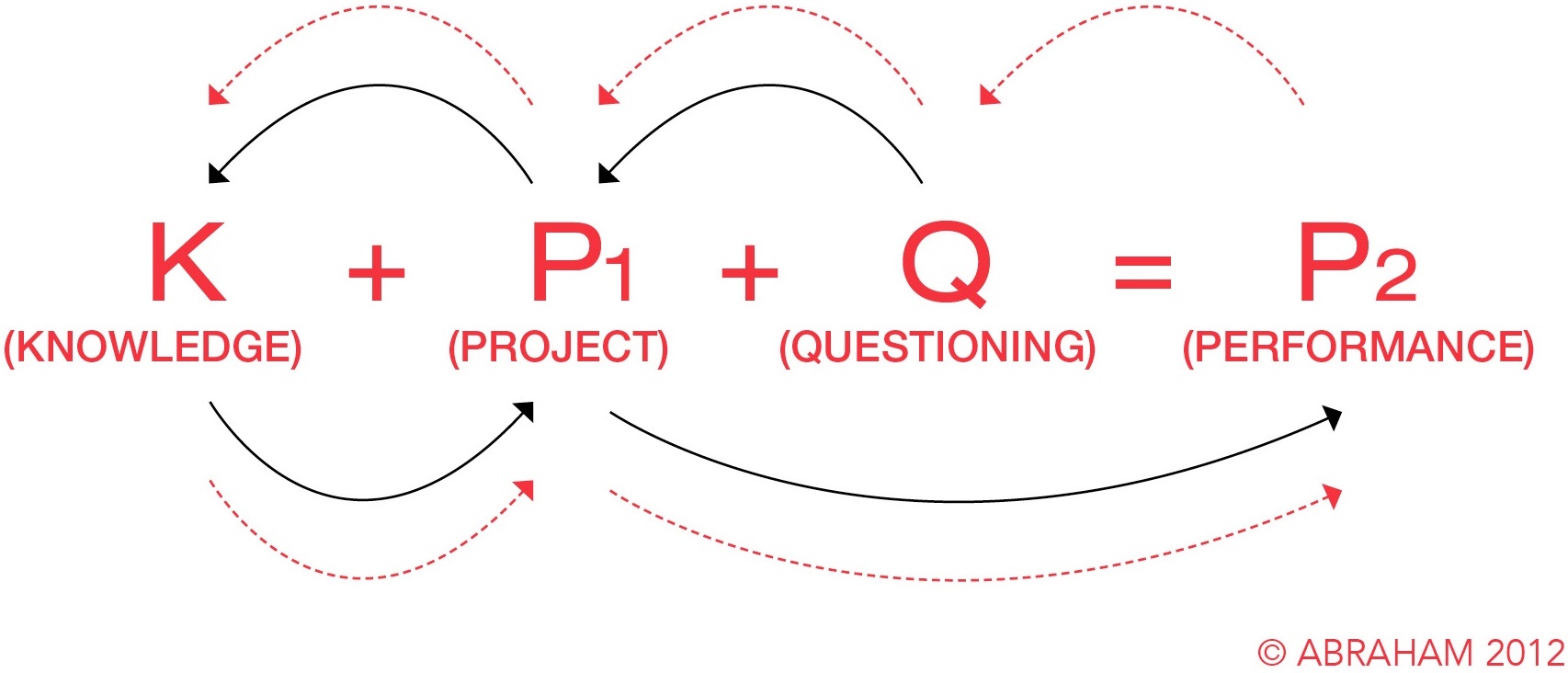
Knowledge
Reflect and apply relevant knowledge in the planning and implementation of a change project
Project (Critical Reflection)
Critically reflect on a project to address a problem or need in the organisation
Question
Question how to solve a problem by searching for ideas to help plan a change project
Performance Outcomes
Achieve project outcomes, process outcomes, and learning outcomes
WAL in Action
Hear how Work-Applied Learning has positively impacted organisations and workplaces
Learn More
Resources to deepen your understanding of Work-Applied Learning
Work-Applied Learning for Change Leaders
Author: Selva Abraham
A comprehensive blend of WAL concepts and practice, combining theoretical framework with practitioner experiences from Australia and internationally.
View PublicationsJournal of Work-Applied Management
Published by: Emerald Publishing
An online journal for experts to share findings and theories on work-applied management research. ISSN: 2205-2062
View JournalReady to Apply WAL in Your Organisation?
Explore our programmes designed to implement Work-Applied Learning at every level.
Learn About WAL Step by Step
An interactive guide through the Work-Applied Learning model — based on the overview video
The Creative Learning Process
How WAL participants think, learn and create change — drawn directly from the WAL overview
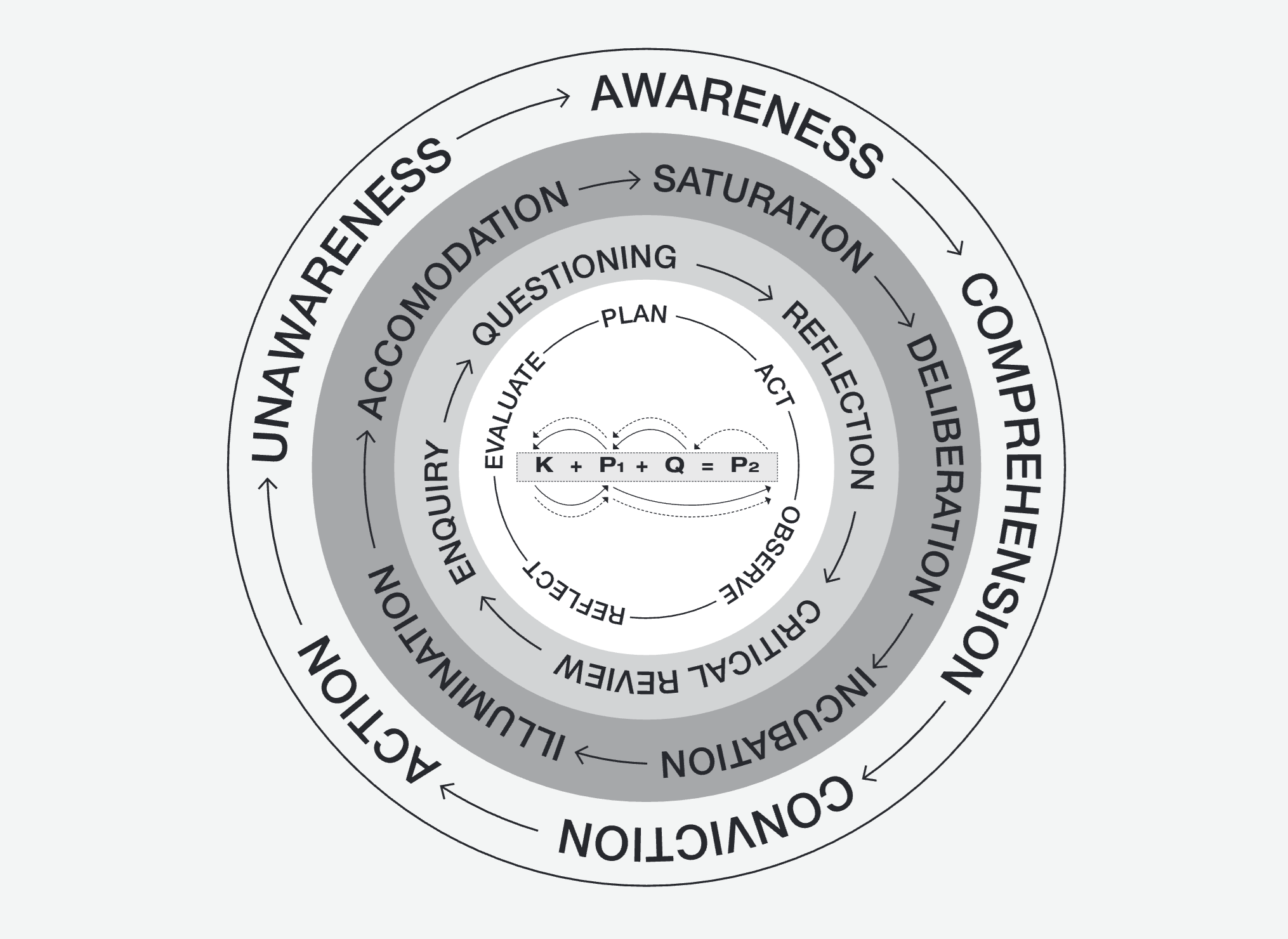
The WAL Creative Learning Process — explore each element interactively using the tabs below
As WAL participants question (Q) against their project (P1), they move through five stages of creative thinking. Click each stage to understand what happens at each point in the creative learning cycle.
Saturation
You become thoroughly familiar with the problem. This deep immersion in the challenge — its context, history, constraints and stakeholders — builds the foundation for everything that follows. Nothing is rushed; total familiarity comes first.
As people move through the creative thinking stages, they simultaneously progress through a journey of growing awareness. Click each stage to follow their transformation from not knowing to taking confident action.
Unawareness
At the outset, people may not fully recognise the nature or depth of the problem facing them or their organisation. This stage represents the starting point — before WAL learning has begun to illuminate the challenge.
Awareness
Through immersion in the problem (saturation) and the application of existing knowledge, participants come to truly see the challenge in front of them. They recognise what needs to change and why it matters.
Comprehension
Awareness deepens into understanding. The participant comprehends not just what the problem is, but how it connects to the broader organisation — its systems, people, and processes. Knowledge (K) and project reflection (P1) combine to generate real insight.
Conviction
Understanding evolves into belief in a course of action. Through deliberation, questioning (Q), and illumination, the participant becomes convinced of the approach they need to take — moving from passive learner to committed change leader.
Action
Finally, conviction leads to decisive action. The participant implements their work-based project, driving real change in the organisation. This is P2 — performance outcomes achieved through the full WAL learning cycle.
WAL captures the cyclical learning process through action research — a continuous loop that drives projects forward. Click each step of the cycle to understand how WAL participants learn and create change.
Cycle
Plan Your Change
Define the problem (P1), gather existing knowledge (K), and design a project plan to address the challenge. Clear planning sets the direction and intent of the work-based change project.
The WAL Model
Click each element to explore the core components of Work-Applied Learning
Work-Applied Learning Model
The WAL model positions the workplace as the crucible of learning for change. It has been specifically developed for managers, leaders and entrepreneurs to learn, reflect, introduce change, and be effective in their organisations or communities.
- Integrates Action Research, Action Learning & Reflective Practice
- Grounded in real work-based change projects
- Enables learning at individual, team & organisational levels
- Leads to internationally recognised WAL certifications
← Click any element to explore

.jpeg)